UTC - IEEE Robotics Club
University of Tennessee in Chattanooga - Spring 2023
Christopher Harmon, Thomas Clemmons, Tahj Taylor, Nate Hawkins, Deimer Ordonez Gomez, John Lazenby
OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision) is a free and open-source library of programming functions mainly aimed at real-time computer vision. It has become one of the most popular and widely used computer vision libraries, with applications in a wide range of industries, including robotics, augmented reality, and the automotive industry, to name a few.
One of the core functionalities of OpenCV is its ability to detect and track objects in a video frame. This ability is crucial for many computer vision applications, including object recognition, motion tracking, and even autonomous driving.
The process of object detection and tracking in OpenCV can be broken down into several steps.
First, OpenCV takes in the incoming frame data and converts it into images. This conversion process is critical for the rest of the object detection and tracking pipeline, as it allows OpenCV to perform image processing on the frame data.
Once the frame data has been converted to images, OpenCV applies color thresholding.
Color thresholding is a technique used to isolate specific colors in an image. In the context of object detection and tracking, color thresholding is used to isolate the object of interest from the rest of the image.
OpenCV then looks at different hue values and isolates those that correspond to the object of interest. The resulting image is then blurred to remove noise. Blurring might seem counterintuitive, but there is often a lot of noise in images that can interfere with object detection and tracking. By blurring the image, OpenCV is removing any high-frequency noise that might be present in the image.
OpenCV performs further morphological operations to remove noise from both within the shape's contour and the surrounding environment. These operations are designed to minimize false positives by removing any additional noise that might be present in the image.
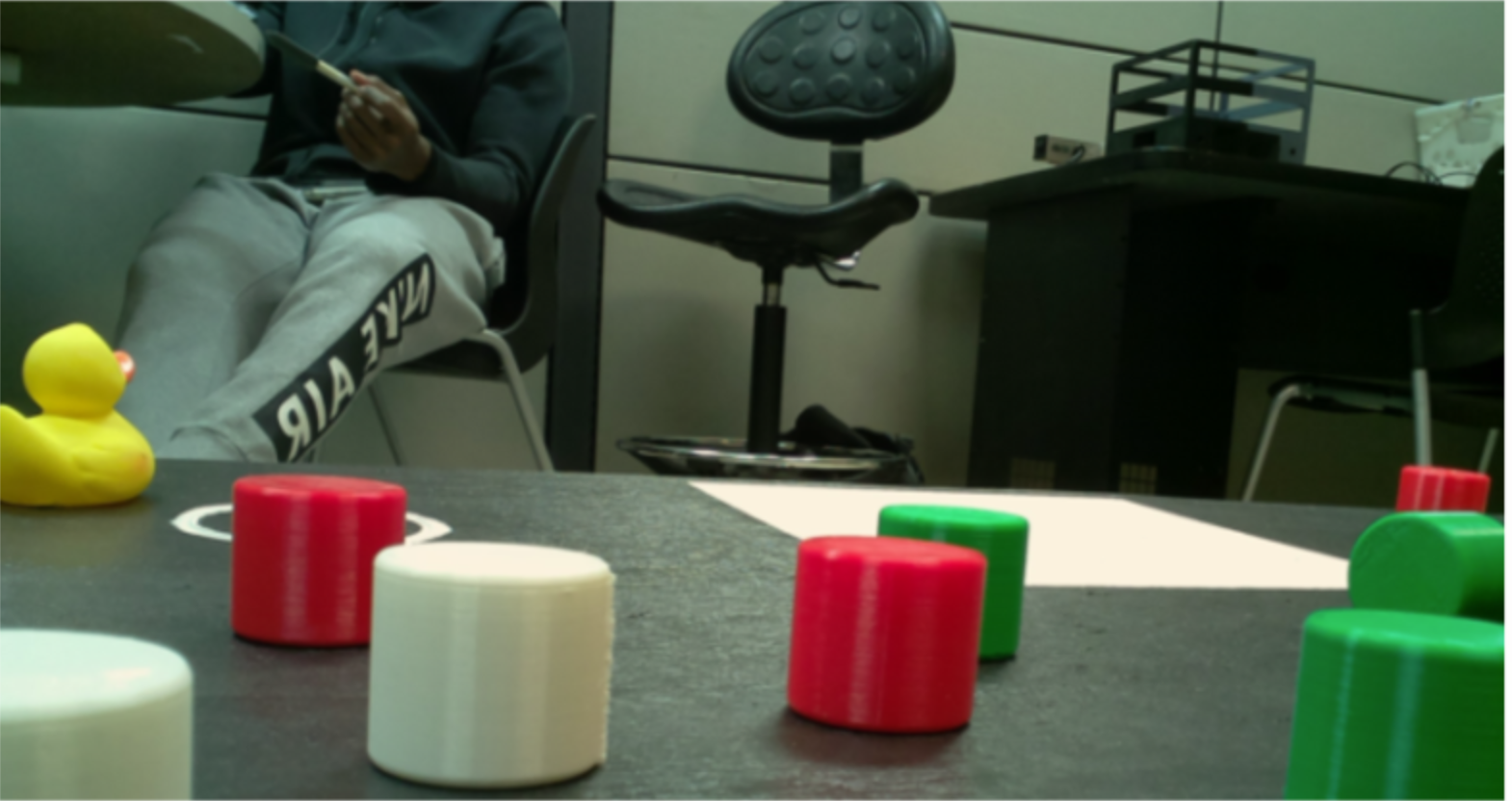

Raw Image
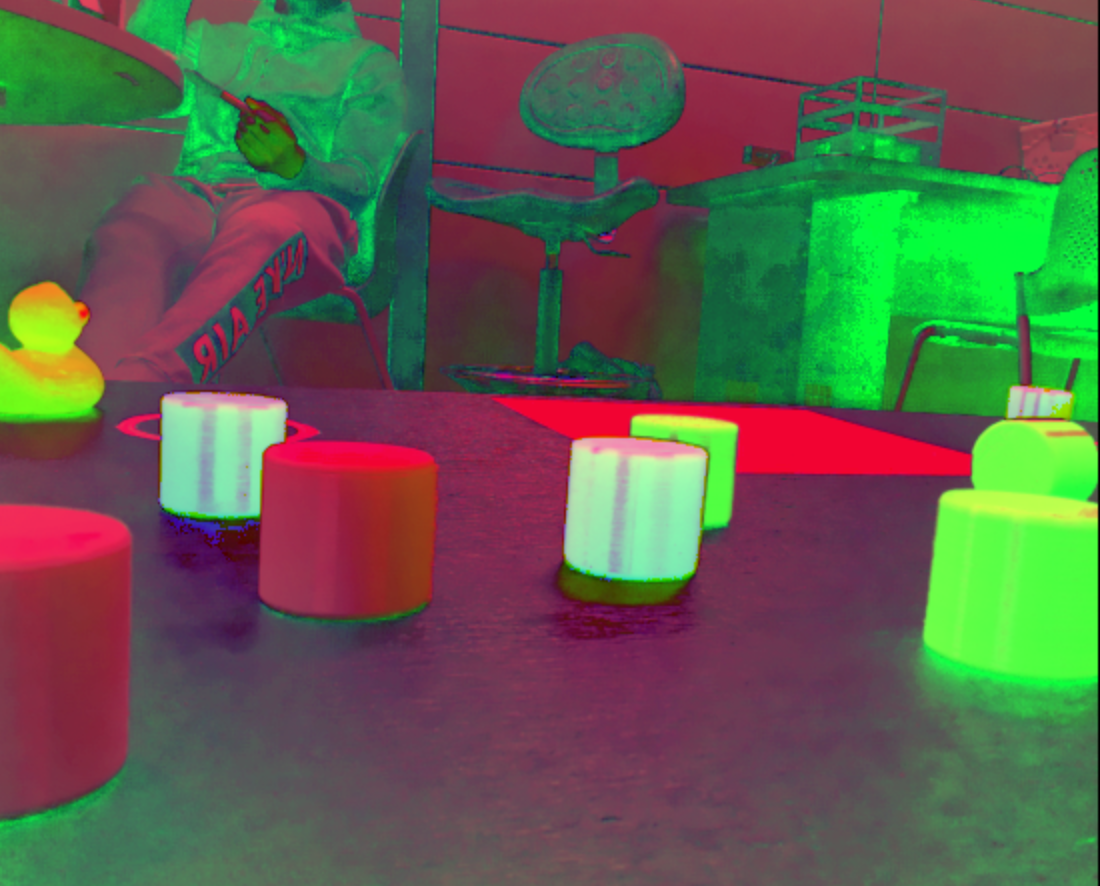

Hue Space
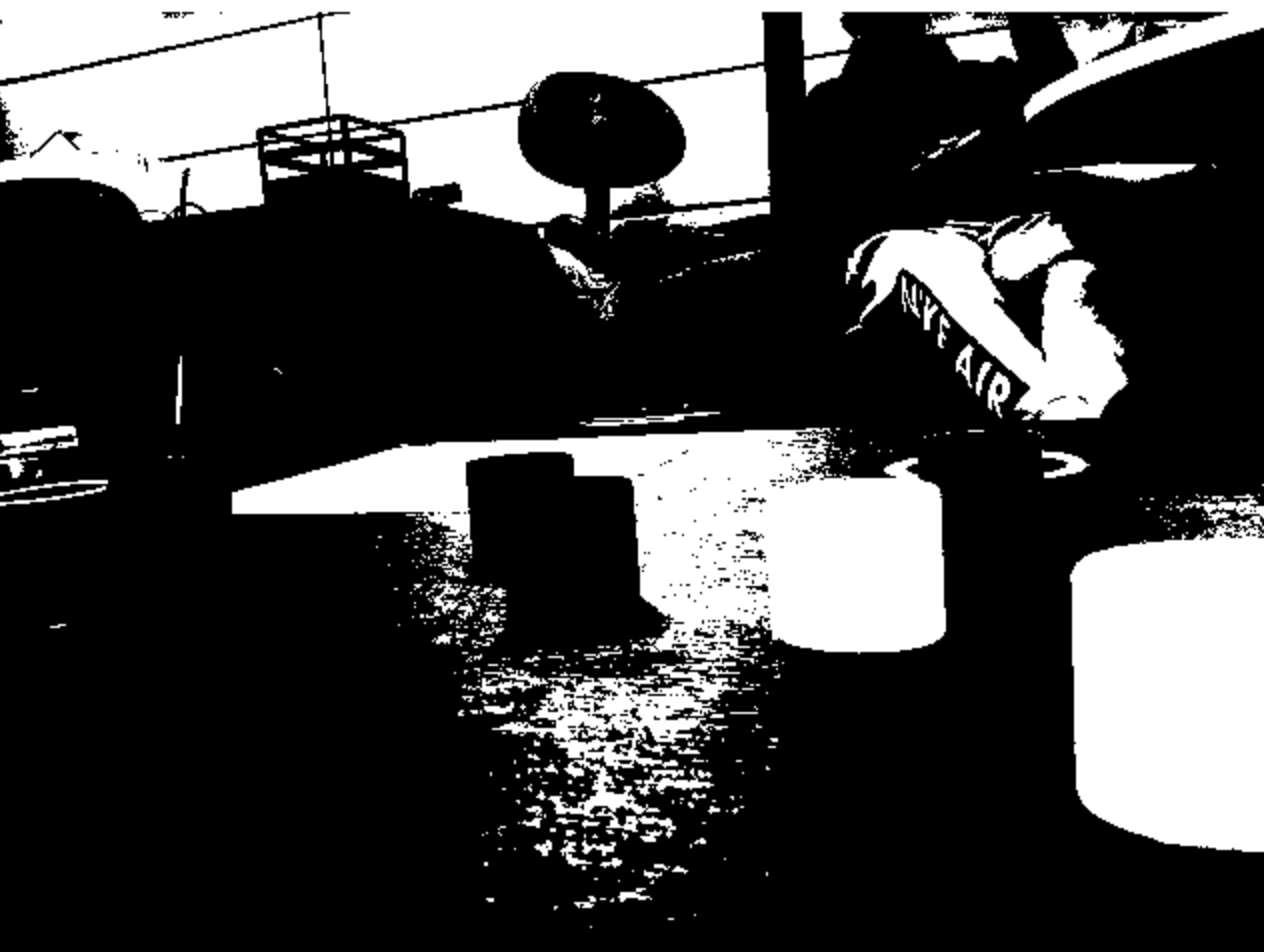

Mask
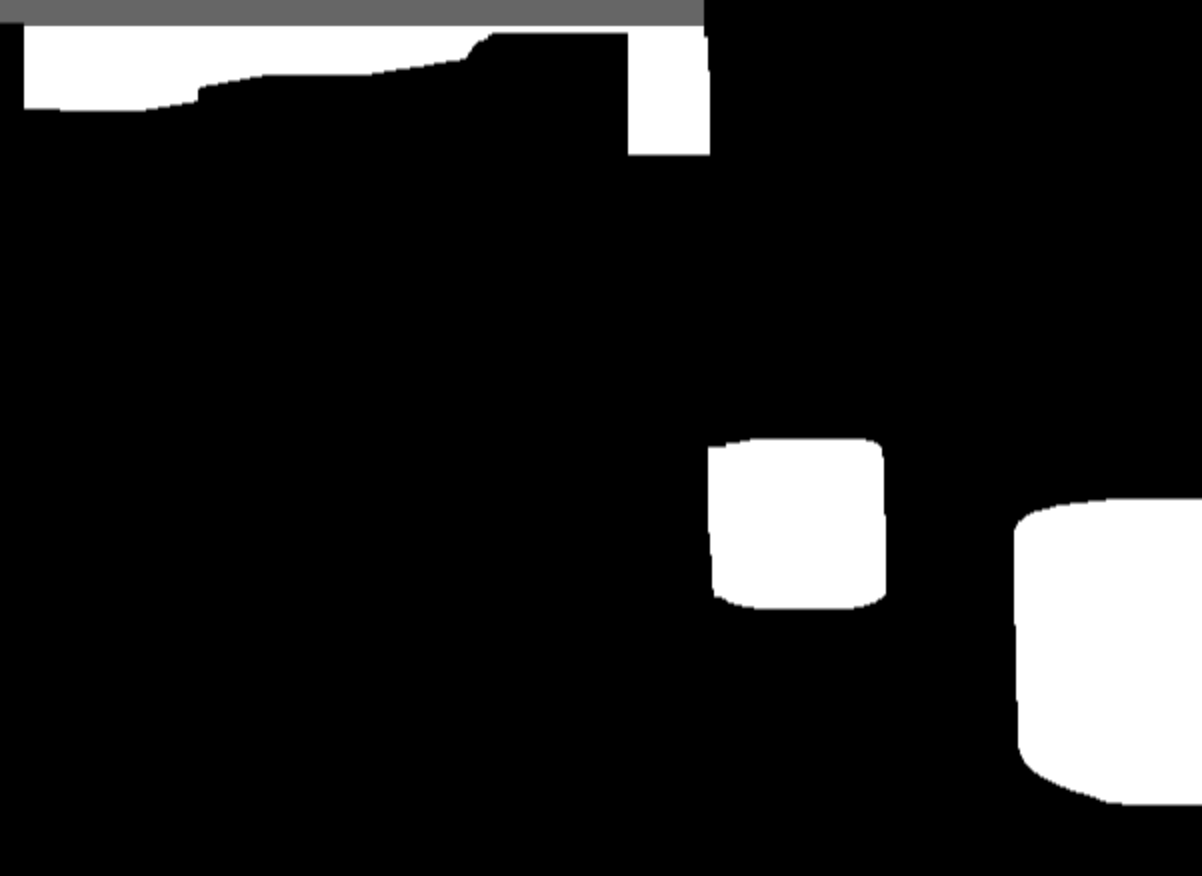

Morphology
Canny Edge Detection
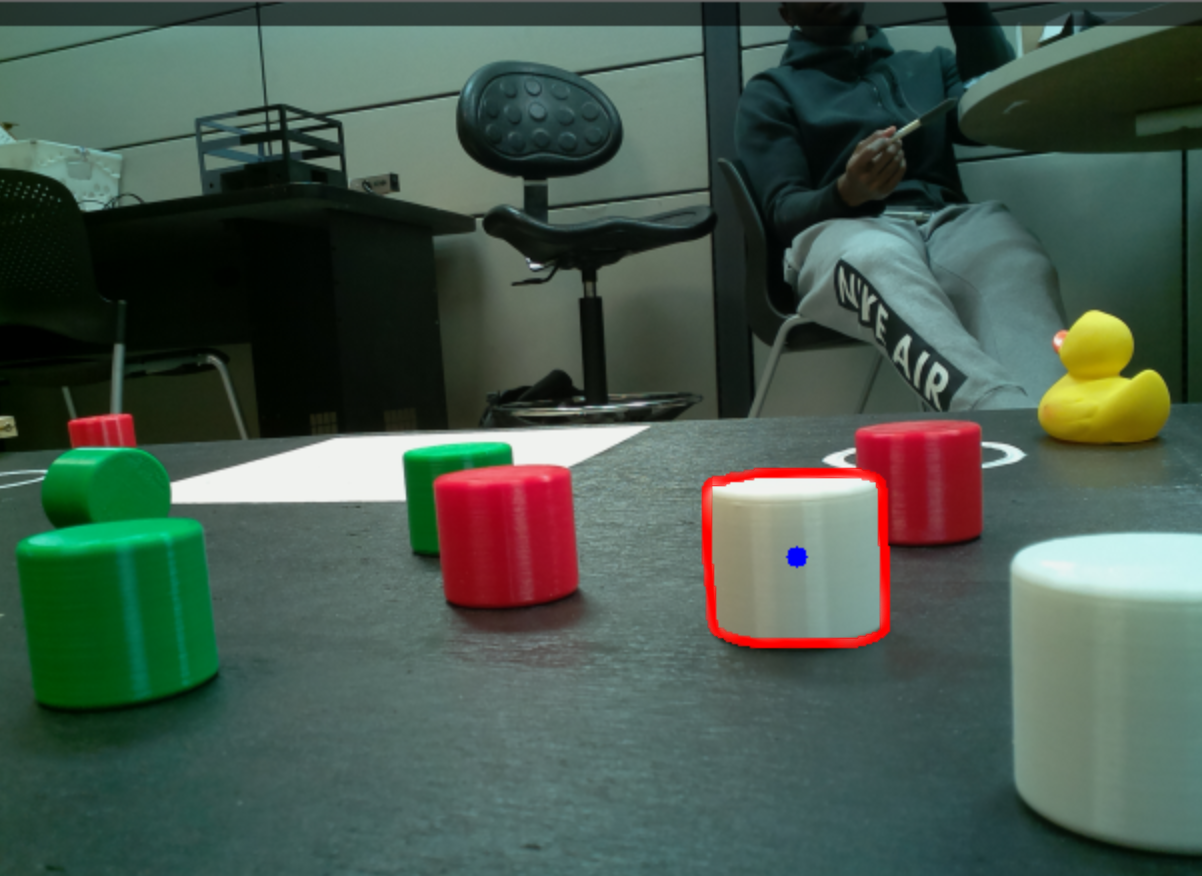

Final Result
Next, OpenCV performs contour detection, this is the process of finding the boundaries of shapes in an image. In the context of object detection and tracking, contour detection is used to identify the boundaries of the object of interest.
OpenCV then calculates the centroid of each contour. The centroid is the geometric center of the object, and it is calculated by taking the average of all the pixels in the contour. OpenCV uses the centroids to track the object as it moves through the frame.
Finally, OpenCV identifies the object with the largest centroid per area, locks onto it, continues to track it.
The ability of OpenCV to detect and track objects in a video frame is crucial for many computer vision applications. For example, in robotics, object detection and tracking are critical for navigation and object manipulation. In augmented reality, object detection and tracking are used to overlay digital content onto real-world objects. In automotive, object detection and tracking are used for collision avoidance and autonomous driving.
Moreover, OpenCV's object detection and tracking capabilities are highly customizable. We can adjust the parameters of each step in the object detection and tracking pipeline to achieve the best results for our specific use case. This flexibility makes OpenCV a powerful tool for CATNAV's vision system.





